The increasing disparity between the rising number of medical graduates and the restricted growth of residency programs presents a significant challenge. Many new doctors face a scenario of being “persistently unmatched,” coupled with considerable financial debt. This predicament underscores a critical aspect of healthcare credentialing – the path to becoming a fully accredited medical professional is marred by considerable obstacles, impacting the integration of new doctors into the healthcare system. Meticulous credentialing is vital to averting revenue losses, ensuring healthcare providers are appropriately certified and authorized to deliver care and obtain payments from insurance entities. This guide delves into the significance of credentialing in bolstering the financial robustness of healthcare organizations.
The Pillar of Credentialing
Credentialing in healthcare transcends simple qualification confirmation. It’s pivotal for assuring safe, superior medical care. This process entails a detailed evaluation of a provider’s educational background, experience, and skills, conferring clinical privileges solely to those adequately qualified. However, overlooking the depth of credentialing carries substantial financial risks, potentially tarnishing the institution’s reputation. It may also lead to legal repercussions, substantial fines, and, in severe instances, criminal charges. Conversely, a thorough and ongoing credentialing process is crucial. It encompasses an extensive review of a practitioner’s credentials and continuous appraisal of their performance. This not only secures high-caliber care and clinical distinction but also enhances patient outcomes. Such a stringent methodology solidifies the healthcare organization’s market standing. Ultimately, a healthcare organization’s success is intricately linked to its credentialing practices. Overlooking this critical element can cause financial and operational setbacks, while a diligent and proactive approach can foster ongoing success and expansion. Therefore, healthcare establishments must acknowledge and tackle the vital role of comprehensive credentialing in sustaining their financial stability.
Grasping the Credentialing Procedure
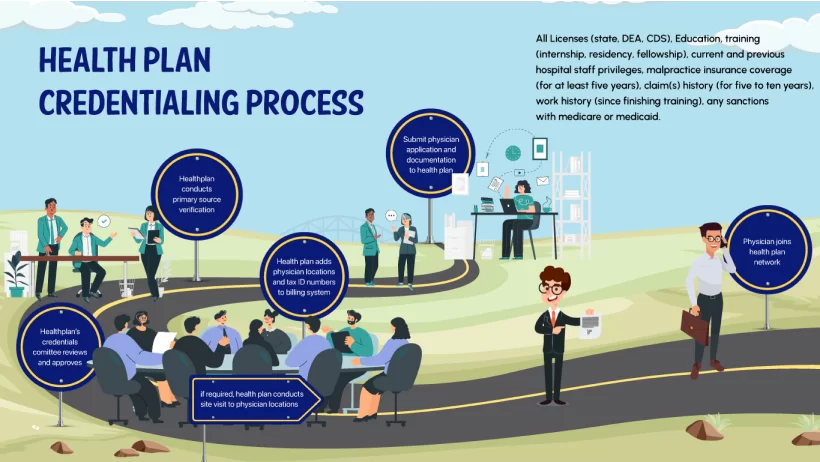
Credentialing involves numerous phases:
Gathering Essential Documents:
This initial phase encompasses collecting a wide array of documents that verify the provider’s qualifications and professional background.
List of Documents to be submitted:
- Medical license.
- Medical school information.
- Internship, Residency, Fellowship information.
- Board certifications.
- Provider’s CV.
- License to practice.
- National Provider Identifier (NPI) number.
- License history.
- Insurance information.
Primary Source Verification (PSV):
Essentially, this involves directly verifying the healthcare professionals’ credentials, like education, licenses, and certifications, from the original sources for authenticity.





The Impact of Comprehensive Committee Review
Committee Review is a formal process where a panel, typically consisting of seasoned healthcare professionals and administrative staff, scrutinizes the credentials of healthcare providers. This review is an exhaustive analysis of a provider’s education, training, experience, and any other relevant qualifications.
The Influence of Committee Review in RCM

Ensuring Quality and Competence of Providers
This review ensures that only qualified and competent providers are permitted to offer care, upholding the standard of healthcare services.

Regulatory Compliance and Accreditation:
Accurate and thorough credentialing, including Committee Review, is often required for compliance with healthcare regulations and accreditation standards. This process aids healthcare facilities in avoiding legal and financial pitfalls.

Risk Management and Patient Safety:
By rigorously vetting providers, the committee helps mitigate risks associated with inadequate care or malpractice, protecting both patients and the institution from potential legal issues.

Streamlining Billing and Reimbursement:
Proper credentialing, confirmed through Committee Review, ensures that billing and reimbursement processes comply with regulatory standards, thereby reducing claim denials and optimizing revenue flow.

Maintaining Reputation:
The credibility of a healthcare institution is closely tied to the quality of its providers. Effective Committee Review helps maintain high standards, contributing to the institution’s reputation for excellence.
Continuous Monitoring: A Key to Healthcare RCM
Continuous Monitoring involves the regular and systematic review of healthcare providers’ credentials to ensure they remain current and comply with relevant standards and regulations. This includes tracking licensure renewals, certification updates, and changes in a provider’s professional status or qualifications.




Credentialing’s Impact on Revenue Cycle Management
Credentialing in healthcare is a pivotal process with extensive impacts on Revenue Cycle Management (RCM). The implications of this process extend beyond simple qualification verification, directly affecting financial viability, compliance, and patient trust. This section will dissect how credentialing influences the revenue cycle and highlight best practices to maximize its effectiveness.
Credentialing’s Influence on Revenue Cycle Management
Eligibility for Insurance Claims: One of the most direct impacts of credentialing on the revenue cycle is its effect on insurance claims. Without proper credentialing, healthcare providers may face claim denials. Insurance companies and government payers require providers to be credentialed as a precondition for reimbursement. Inaccurate or outdated credentialing information can lead to claim rejections or delays, resulting in considerable revenue loss.
Compliance with Regulations: Credentialing is not merely a bureaucratic procedure; it’s a compliance necessity. Healthcare organizations must comply with various regulations and standards set by entities like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the Joint Commission. Non-compliance due to improper credentialing can lead to legal complications, substantial fines, and, in severe cases, loss of accreditation. Such events not only have immediate financial consequences but also long-term reputational damage.
Building Patient Trust: In the healthcare industry, trust is invaluable. Properly credentialed practitioners are more likely to attract and retain patients, directly impacting revenue. Patients often prefer healthcare providers who are credentialed, as it reassures them of receiving care from qualified professionals. Credentialing becomes a marker of quality and dependability, influencing patient choice and loyalty, thereby indirectly enhancing revenue.
Best Practices in Credentialing
To improve the efficacy of the credentialing process and its positive impact on RCM, healthcare organizations should follow these best practices:
Timely Re-credentialing and Monitoring: Avoiding lapses in credentials is critical. Continuous monitoring and timely re-credentialing ensure uninterrupted billing and compliance.
Automation and Credentialing Software: Utilizing technology can significantly simplify the credentialing process. Credentialing software automates many aspects, reducing manual errors and saving time, thereby boosting efficiency and reliability in the revenue cycle.
Regular Communication with Providers: Keeping healthcare providers updated about their credentialing status is crucial. Proactive communication can quickly resolve any arising issues, preventing delays in the credentialing process.
Compliance with Changing Regulations: The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, with frequent changes in laws and regulations. Staying updated and ensuring compliance with these changes is essential to avoid penalties and ensure continuous revenue flow.
The Future of Credentialing
Looking forward, credentialing is poised to evolve with advancements in technology and changes in healthcare regulations. Predictive analytics, AI, and further automation will streamline the credentialing process, making it more efficient and less prone to errors. Additionally, a more interconnected healthcare system could lead to standardized credentialing processes across states and institutions.
Effective credentialing transcends being a bureaucratic requirement; it’s a strategic instrument in healthcare RCM. By ensuring proper credentialing, healthcare organizations can prevent revenue loss, maintain compliance, and boost patient trust. As technology continues to progress, credentialing processes will become more streamlined and efficient, further bolstering the financial health of healthcare providers. In an era where financial stability is as vital as the quality of care provided, embracing the power of effective credentialing is not just a choice but a necessity for a flourishing healthcare industry.

