As the world continues to shift online, even traditional brick-and-mortar businesses will have to invest more in their digital presence. But how do you stand out among a sea of competitors who are also vying for the same consumers as you are? That’s where SEO optimization for websites comes in.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of optimizing your website for a search engine’s page ranking factors so it can rank higher in search results and drive more traffic to the website.
When you start creating an SEO strategy for your website, there are two aspects you need to focus on: On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO. As the names suggest, on-page SEO includes optimization done on the website that tells Google about the quality of your website, while off-page SEO is optimization done through links on external pages (using SEO link building) that tells Google about the authority of your content.
Let’s dive deeper into what on-page and off-page SEO cover and what they mean for your business.
Guide to on-page SEO
On-page SEO optimization for a website is something that you have complete control over. Google prioritizes the user experience over all else and therefore, it ranks websites higher that offer a smooth browsing experience. This is why when you’re optimizing your website, you aren’t just doing it for a higher search ranking, you’re also looking at website design to ensure a seamless experience for your website visitors. This can ultimately result in a longer time spent on the page per user and higher conversions. Google interprets the time a visitor spends on the page as an indication of how useful they found the content.

-
Proper heading tags
A heading hierarchy helps structure your content on a page, making it easier for users to skim through it and understand the context. Google analyzes the structure of headings on your page to determine readability. Every page should have only one main heading and this will use the H1 tag. Subsequent headings should have H2 tags and any sub-points under them can have H3 or H4 tags. Headings are also a great way to include your keywords. The H1 tag should always have your primary focus keyword while H2 tags can have your secondary keywords.
-
Page load speed
Research has shown that the chances of a user bouncing from a website is around 90% higher if the page takes more than 5 seconds to load. A slow page load speed can prompt Google to downrank your website.
How do you find out if your website speed needs to improve? Google provides a free tool called Pagespeed Insights that will analyze your website load time and will identify factors that contribute to it. For example, it might suggest reducing the size of images and minifying HTML files to improve page speed.
-
Quality of page content
Quality content is arguably the single most important page ranking factor for Google. Google wants to provide users with the most relevant content for their search queries. Even if your website ticks every SEO box but you don’t have high-quality content, it will struggle to rank higher. One way to signal to Google about the quality of your website content is to have at least 500 words on each page. Anything lower and Google will flag your website as having ‘thin content’.
Content should also be keyword optimized but ensure that your keywords are not force-fitted and aren’t too repetitive. If you fall victim to ‘keyword stuffing, your search ranking will be impacted. This is a factor that you need to keep an eagle-eye on. Many ‘SEO experts’ working on optimizing your site will stuff keywords onto the page so that it occurs with a very high frequency. However, reading such content, makes it obvious that it is not occurring naturally. Natural usage of keywords will be seamless with the existing content and promote usability.
-
Website mobile-friendliness
Around 80% of all searches now take place through a mobile phone. As mobiles become more pervasive, Google is prioritizing the mobile browsing experience over the desktop. To ensure your website is mobile-friendly, check the page load time for mobile users (both over 2G and 3G connections). The overall design and layout of your website should also be optimized for mobile. Such websites have a mobile-first design that is then adapted to a desktop screen size. The alternate happens in responsive web design.
-
Internal linking
Your website pages should not exist in silos. Always ensure that you link to relevant pages from every page of your website. The text that is interlinked is known as the ‘anchor text’ and should ideally contain the keyword you’re targeting.
-
Schema markup
Structured data or ‘schema’ helps Google’s bots understand the purpose and structure of your content, which makes it easier for them to crawl and index your page. Specific types of schema can also help you show up in relevant SERP features. For example, adding an FAQ schema to an FAQ page can help relevant answers show up in the answer box feature when a user searches for a similar query.
Apart from these essential on-page factors, Google has also started to prioritize two additional ranking factors: core web vitals and page experience.
Core web vitals are a set of features that Google believes are essential for a smooth user experience. These include Largest Contentful Paint (the time it takes for the initial content to load on a page), First Input Delay (how long it takes for the website to respond to an action by a user) and Cumulative Layout Shift (measures visual stability i.e. how much the layout of a page shifts as the page fully loads).
Page Experience is an umbrella term that includes several ranking factors that contribute towards a positive browsing experience. This includes page speed, mobile-friendliness and the HTTPS certificate.
All you need to know about off-page SEO
Off-page SEO involves boosting the authority of your own website using signals from external websites. Backlinks, or links from external websites pointing to your website, are the foundation of off-page SEO. Google views every backlink as a token of trust, the assumption being that if other websites cite your website as a reference, the content you offer must be authoritative. The more backlinks you have, therefore, the higher your website authority (known as Domain Authority or Domain Ranking) increases and the higher you rank.
It’s important to remember that apart from the mere number of backlinks, Google also focuses on the quality and relevance of the backlinks you have. In other words, you should have backlinks from websites that also have a high Domain Authority and are similar to the topics your website deals with. This is what a business must watch out for – many of the backlinking specialists they hire pick websites randomly and not by related topics.
An important point to make here is that there are many guest blogging sites that you can pay to add your content with a backlink. However, Google also looks at the ratio of the number of links pointing to these sites compared to the links going out from these sites. Normally such sites have more links going out and Google marks them as spammy sites and you won’t get any advantage by posting here.
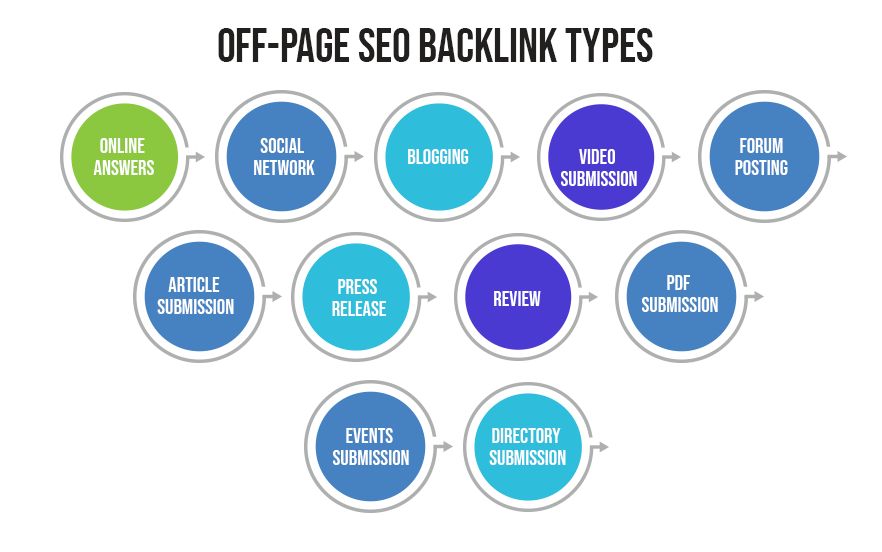
Some of the ways to start SEO link building for your website:
- Posting high-quality content: Quality content is a great way to gain organic backlinks. Original research or authoritative content like whitepapers and infographics can be used as citations or examples when other websites cover a similar topic.
- Guest blogging: This is when you collaborate with other websites to publish an opinion piece or blog and then include a link to your website from the article.
- Unlinked brand mentions: Websites could already be mentioning your brand name without linking to your website. If you find instances of this, you can reach out to the website owner and request a backlink.
- Social media and influencer marketing: Creating social media posts that link to your website is a great way to gain backlinks. You can also collaborate with influencers who can post about your brand on their website and social handles.
As the number of backlinks generated increases, you should also check the web page rank for your website. You should notice a positive correlation between the two.The majority of backlinks you build must beThe interlinked textSEOmany basic factors remain ‘Do follow’ backlinks rather than ‘Nor Follow’.
To know if the website you are getting a link from provides a ‘Do follow’ link, right-click on the page and go to ‘view page source’. Search for the text you have linked and see if this code is attached to it: rel=”nofollow”. If it is a do-follow link then this code won’t be there.
On-page and off-page SEO are equally vital to improving the overall search rankings for your website. If you are starting SEO optimization for a website from scratch, then a good approach is to focus on on-page SEO first before moving to off-page. This allows you to build a healthy website that will lay the foundation for subsequent SEO efforts. To monitor whether your SEO efforts are paying off, you should routinely check page rank for target keywords. There should be a continuous upward trend that signifies that your SEO strategy is working.
To discuss a SEO strategy for your business website, reach out to our website specialists today.

Karen Jain
Karen brings her decades-long experience in content and digital marketing to helping global brands to showcase their expertise. When she isn’t writing or caught up in being a digital marketing evangelist, you will find her passionately involved in animal rescues.