If your organization is already using RPA, the probability is that you are discussing upgrading your business process automation from RPA to intelligent automation.
For those not familiar with these terms, let’s get you quickly up to speed. RPA automation when it was introduced in the early 2000s was a breakthrough technology. In the course of these years, it is no exaggeration to say that companies that have implemented RPA have probably saved millions of hours of manual work and that millions of documents have been processed, data updated or invoices generated. This also means that there have been a lot of dollars saved or added to the company’s bottom line. However, RPA has its limitations and one of them is that it is not scalable and maintenance can eat into the profits of running RPA business processes. Hail then to the new kid on the block – intelligent automation that uses AI and machine learning along with deep learning.
Let’s dive further into the difference between RPA and IA and how to adopt an intelligent automation strategy.
Difference between RPA Automation and Intelligent Automation
The robot in robotic process automation is not a physical robot but a software bot that can automate mundane routine tasks. RPA is a business process automation technology that will exactly mimic how humans will interact with software. It uses graphical user interfaces (exact position of information on a screen) so if there is a change to the user interface then the RPA process will break down.
These RPA bots can only follow rule-based processes and they are unable to extract meaning from the images or documents they are processing. RPA is best suited for automating individual tasks. It will be a herculean task to automate an entire process, for instance, onboarding a new customer into a bank. This would require setting up exhaustive linear decision trees for every possible outcome. This would take a long time to set up and if there is any change such as new initiatives added, then the code would have to be updated every time.
This is why RPA is now extended to include intelligent automation. RPA and IA are two different technologies that can coexist to create a more robust platform
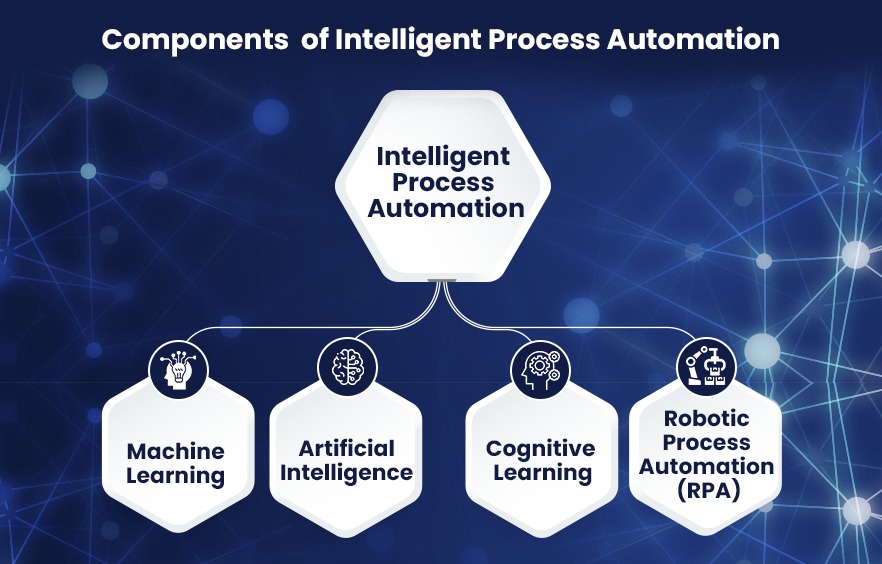
What this does is allow RPA to be the ‘muscle’ that does the grunt work while the decision-making tree is powered by Artificial Intelligence that includes machine learning and natural language processing – the components of intelligent automation.
How RPA and IA together can extend capabilities
Most enterprises that have implemented RPA have reached the threshold beyond which RPA cannot deliver any incremental value. Business leaders are realizing the need to use automation as a business strategy to deliver greater value rather than just a tactical shift.
This example can better illustrate why the business strategy should power a shift to intelligent automation. The healthcare sector is one of the best illustrative examples for the IA use case.
1. RPA was already implemented for the front desk staff who used it to organize patient details and move data to the payment process.
2. The clinicians though might use a different process to handle clinical notes and enter them into files in the EHR. The clinicians’ workflow will use intelligent automation tools like OCR along with natural language processing for the clinical notes.
3. These two are different processes but the data needs to be consolidated between the general files uses by the front desk and the clinical notes from the physicians’ system. This had to be done manually but also became the best use case for intelligent automation.
4. The gap between the two processes was filled by intelligent automation that can bring the two processes together into one seamless continuity. IA brings in a native intelligence that can automate decisions based on structured and unstructured data (such as images, texts and videos)
This is what hyperautomation does – it makes interactions between human workers and their digital co-workers possible. Unlike in RPA, it need not work in isolation and there can be a hand-off between automated processes and humans.
Intelligent automation has the ability to self-manage. For example, it can organize data as well as make inferences from it and then act on these decisions – all the while becoming more and more intelligent as it learns continuously from transactions that are occurring.
How to move strategically from RPA to IA
Organizations keen to implement intelligent automation will first start with a small use case and scale it from there as they become confident of success. However, whether starting big or small, identifying the processes to automate has to be the initial step. The criteria should be which one will best deliver on business objectives. Here is a quick overview of how businesses start the intelligent automation process.
Identify business objectives:
For a business to develop an intelligent automation strategy, it is first vital to understand how different business workflows and technologies can be linked together to accomplish a specific goal. Every business will have thousands of such possible combinations but identifying the right combinations to automate must be entirely dictated by business objectives and desired outcomes. The most common business objectives are
- Operational savings by increasing staff efficiency
- Impact revenue growth by automating customer-facing processes to improve customer experience
- Improve data security since manual processes can open the door to security risks. Automation can improve compliance and reduce data leaks.
Assess each step of the business process:
Once an initial list of processes are identified, analyze those that are subject to frequent changes or have more than 10 ways of executing the same process. While intelligent automation is self-aware and can self-manage, still the business process needs to eliminate any redundant processes. A streamlined process has a greater chance of succeeding.
Put in place a data strategy:
A key element in intelligent automation is access to high-quality operational data. The cognitive components of IA (ML, NLP and deep learning) can train the algorithms to look up extra data to create new patterns to come up with the best action in an unfamiliar situation. When data is the key then the existing cloud data architecture might need to be re-examined as well as an investment made in additional data storage systems in the cloud.
Finally, automation requires that organizations should be in a highly mature stage with well-defined standards and process definitions. Companies with an effective center of excellence will also have a distinct advantage when it comes to implementing intelligent automation.
Talk to our experts to get more insight on how to start your automation journey.