Business process automation (BPA) and workflow automation are related concepts but have distinct differences. BPA and workflow automation often utilize similar technologies and automation tools. For example, both may involve the use of software platforms, robotic process automation (RPA), or other automation technologies. This similarity in the underlying technologies can blur the distinction between BPA and workflow automation.
Different organizations and individuals may use terms such as BPA, workflow automation, process automation, or task automation interchangeably, further adding to the confusion. However, it is important to make the distinction between business process automation and workflow automation.
Highlights
ToggleDifference between Business Process Automation(BPA) and Workflow Automation
In an overarching view, the difference between business process automation and workflow automation is that the latter can be considered a subset of BPA.
The way BPA and workflow automation are implemented can also contribute to confusion. In some cases, organizations may initially focus on automating specific tasks or workflows and gradually expand their automation efforts to encompass larger processes. This evolution in implementation can make it challenging to draw a clear line between BPA and workflow automation.
BPA and workflow automation share common benefits, such as increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved productivity. The overlapping advantages make it difficult to differentiate between the two concepts, especially when organizations are primarily focused on achieving specific outcomes rather than adhering to specific terminology.
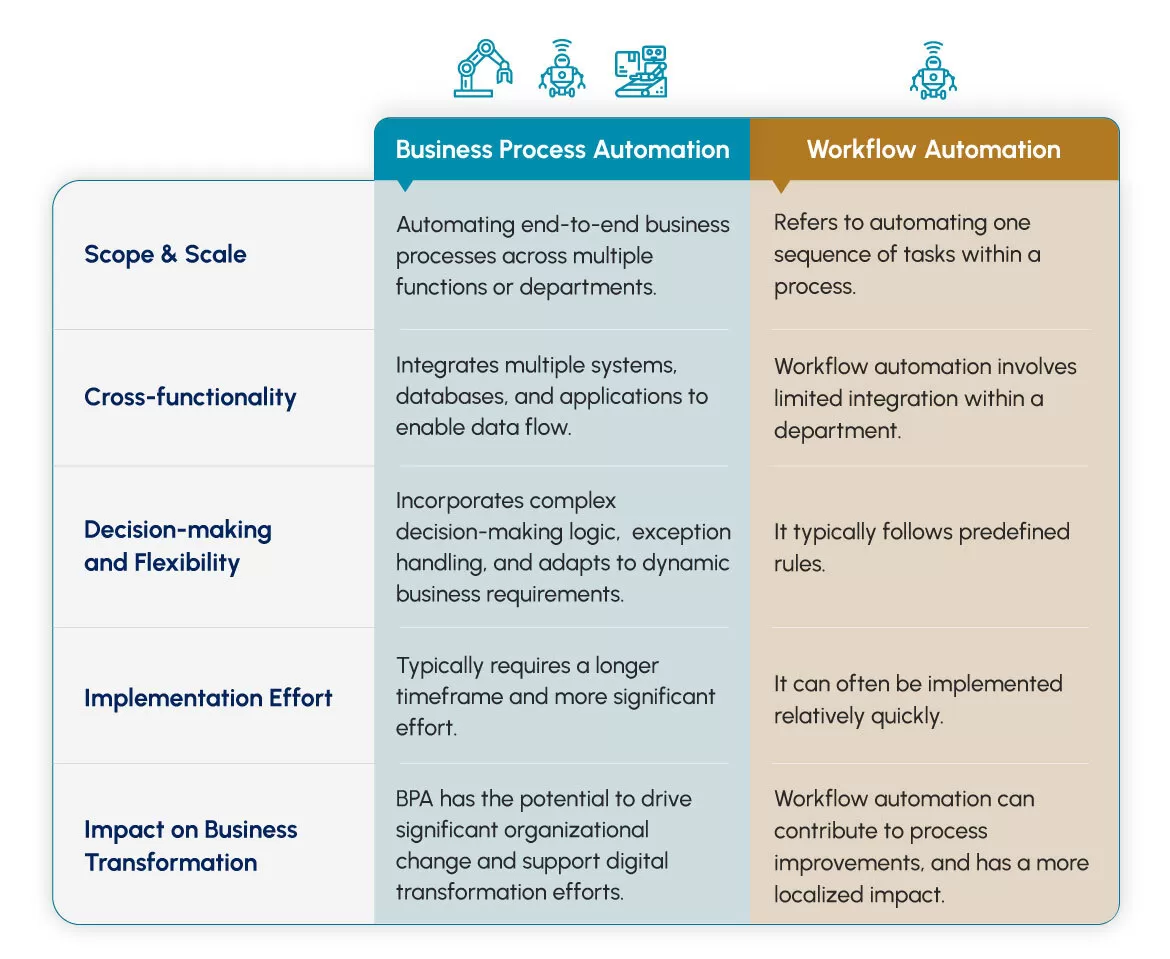
To overcome the confusion, it is important to understand the key differences between BPA and workflow automation, such as the scope of automation (entire process vs. specific tasks), the level of integration (cross-functional vs. task-based), and the focus on process optimization (end-to-end vs. task-level).
Let’s define each term and highlight their disparities:
What is Business Process Automation (BPA)
Business process automation refers to the use of technology to streamline and optimize complex, end-to-end business processes. BPA aims to automate repetitive tasks, reduce manual intervention, and increase operational efficiency. It focuses on transforming entire business processes by integrating various systems and tools to achieve seamless automation. BPA often involves the use of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic process automation.
BPA typically encompasses the following elements,
Integration Automation:
BPA integrates multiple systems, databases, and applications to enable data flow and process synchronization. This is the reason it is also referred to as integration automation.
Cross-functional Automation:
BPA automates entire business processes across different departments or functions within an organization.
Process Optimization:
BPA aims to enhance process efficiency, minimize errors, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity.
End-to-End Automation:
BPA addresses the complete lifecycle of a process, from initiation to completion, involving various stakeholders and activities.
What is Workflow Automation?
Workflow automation focuses on automating specific tasks or activities within a given process or workflow. It aims to streamline and expedite individual tasks, often within a defined sequence, by eliminating manual steps and reducing human intervention. Workflow automation typically involves the use of software tools and platforms that enable the design, execution, and monitoring of workflows.
Workflow automation includes the following characteristics,
Task-level Automation:
Workflow automation focuses on automating individual tasks or activities within a larger process or workflow. In short, it means that not all processes in the workflow are automated.
Sequential Execution:
Workflows are typically designed to follow a specific sequence or order of tasks.
Task Assignment and Notifications:
Workflow automation systems assign tasks to appropriate individuals or teams and send notifications or reminders.
Conditional Logic:
Workflows can incorporate conditional rules or decision points to determine the next steps based on certain criteria.
Tracking and Reporting:
Workflow automation systems provide visibility into the progress of tasks, allowing for tracking and reporting on key metrics.
Business Process Automation (BPA) vs. Workflow Automation
There is nothing like a practical implementation of BPA to understand the different terminologies.
Business Process Automation (BPA) example in HR Systems
Let’s consider the process of employee onboarding in a company. BPA can be applied to automate the entire onboarding process, which involves multiple departments and activities. Here’s how BPA can optimize the process:
Integration:
BPA integrates HR systems, payroll systems, and other relevant databases to ensure seamless data flow between departments.
Cross-functional Automation:
BPA automates activities such as creating employee profiles, initiating background checks, assigning company resources (e.g., laptops, email accounts), and setting up payroll information.
Process Optimization:
BPA identifies bottlenecks and eliminates manual steps, reducing paperwork, manual data entry, and manual approvals.
End-to-End Automation:
as an integrated automation process, BPA tracks the progress of each onboarding task, sends notifications to various stakeholders across business functions, and ensures a smooth onboarding experience for the new employee.
According to a study by Statista, the leading drivers for adopting business process automation are cost reduction (62%) and operational efficiency (56%). Here is an earlier article that explains business process automation and its industry application
Workflow Automation example in customer support workflow
Consider a customer support workflow for resolving customer complaints, it is a popular workflow automation example. Workflow automation can be applied to streamline and expedite the tasks within this process.
Task-level Automation:
The workflow automation system assigns incoming complaints to available support agents based on workload and expertise.
Sequential Execution:
The workflow automation tool guides agents through a sequence of steps, such as gathering relevant information, investigating the issue, and providing a solution.
Task Assignment and Notifications:
The system automatically assigns tasks to agents, sends notifications for new complaints, and escalates urgent issues.
Conditional Logic:
The workflow automation system can include decision points to route complex complaints to specialized teams or escalate high-priority issues to supervisors.
Tracking and Reporting:
The system tracks the status of each complaint, generates reports on response times, customer satisfaction, and identifies areas for improvement.
In both examples, BPA and workflow automation play a role in optimizing processes. BPA focuses on end-to-end process automation and optimization, while workflow automation concentrates on streamlining individual tasks within a process or workflow.
Starting Your Business Process Automation Journey?
In most cases, companies begin to automate their existing workflow processes by focusing on discrete tasks and workflows, Once they are able to evaluate these initial successes, they use it as a foundation for more comprehensive business process automation. Talk to our business process experts today to understand the prevalent best practices that iTech follows that can jumpstart your own success story.