
Due to the increase in the demand for software and applications, the pressure on IT companies to deliver innovative solutions on time is high! Moreover, only a few big companies have the financial and human resource strength to meet the market demands using traditional methods of development. To keep up with the latest digital transformations and offer customers fast-to-market solutions, low-code technology has emerged and is gaining popularity as a game-changer.
With low-code, it becomes easier for developers to create customized solutions and, at the same time, increase productivity.
What is the Low-Code Movement?
No code differs from low code and is directed toward different types of users. No-code is a simple way to build websites as well as other applications using a visual drag-and-drop interface. Compare this with writing tons of lines of code to get the same end result. This is why No-code Low code is considered a great equalizer.
However, no-code platforms do not allow any customization and are aimed at non-developers i.e. business users.
Low code is aimed only at developers or programmers. This is because it allows customization of features for which you need to have technical knowledge. The advantage is that low-code helps coders to work faster.
The main aim of low-code is to reduce the time involved in creating codes from scratch and increase the amount of code that can be reused.
One of the major reasons it is called “low-code” is because low code development is split roughly 80:20 between visual coding and hand coding. In simple words, you build 80% of your application using low code UI and then hand-code to customize your application.
According to Garter:
- 41% of new low-code clients will come from outside IT organizationsby the end of 2025.
- By 2024 low-code application development will be responsible for 65% of application development activity.
Low-code platforms are gaining popularity as they allow businesses to quickly build and deploy applications without needing expensive and time-consuming coding projects. This helps to easily adapt to market changes and transform rapidly based on the needs of the customer, which is a must for digital transformation.
Low Code Development- Use Cases
From smaller businesses to powerful enterprises, all are using low-code development in a variety of ways from online portals to digitizing customer interactions. Here are a few uses cases in different industry sectors
1. Low-code in eCommerce
Low-code eCommerce platforms are becoming more popular because entrepreneurs can quickly get their online store in front of customers. These are some of the common components offered by a low-code eCommerce development platform.
App Development: Every eCommerce store needs an app. Low-code application development allows developers to reuse functional modules that are generic to every eCommerce platform. Because of the drag and drop features, an app can be developed within the shortest time possible
Data integration: Ecommerce deals with large volumes of data coming from different sources such as IoT, social media and big data (including orders and customer info). All these technologies need to be integrated. Low-code platforms provide pre-built connectors that integrate different data sources.
One-click scalable cloud deployment: Cloud services are what have made the digital transformation possible. Low code platforms allow businesses to easily leverage services of cloud service providers like Google, Amazon, Microsoft, etc.
One of the most popular eCommerce websites that have used low-code development is Raylo. They have built the entire platform on low code, including the ability to carry out live stock checks on the products, customer sign-ups, and account management.
2. Low code in Financial Services
Fewer people are visiting physical banks and insurance centers to open an account or do financial transactions. Almost all aspects of financial services have gone digital. What’s more, embedded insurance and banking means that financial data is becoming embedded in third-party consumer apps. In this scenario, low code development is becoming the quickest way for financial services to increase automation and deliver new customer experiences. Here are just a few examples of low-code adoption in the financial sector:
Aggregating financial data: Low code components can aggregate data from multiple sources much faster than if custom code was to be written. Combining data from in-house financial databases as well as third-party sources provides a clearer picture that can lead to better personalization potential as well as investment guidance. Many low-code platforms also provide machine learning models that can quickly show trends for investment opportunities.
Supports a component-based architecture: Both banking and insurance have large enterprise ERPS that can hamper digitalization. These institutions are now beginning to expose their core infrastructure using API-based components for third-party adoption. For instance, when booking a flight ticket, almost always flight insurance is provided as an option. This is embedded insurance through third-party APIs.
These are just a few examples of how low-code is providing a faster adoption of agile solutions. A caveat here is that low-code cannot replace custom software development, particularly in core functionality.
3. Education sector and low-code usage
The pandemic made it obvious to educational institutions how important it is to pivot quickly. Institutions with a modern education ERP like that provided by iTech’s Edumate have an intuitive drag-and-drop interface that allows rapid creation of new functionality. Some examples are as below:
Create a custom calendar: Creating manual timetables and calendars for each course or class can be time-consuming. Using a drag-and-drop interface can speed up the process.
Student forum: Low-code platforms also contain various messaging tools that help to make communication and collaboration easy by bridging the gap between students, parents and the school by creating low-code messaging forums to promote open communication.
One of the education industry’s most popular and successful low-code projects is the University of South Florida. During the pandemic, the top technologist at USF decided to use this technology to implement the digital transformation strategy. This move was very successful, and today USF has been recognized as an innovator in higher education.
4. Software Developers
According to a recent study, 83% of developers experience burnout, 47% feel it is due to the workload, and the other 31% cited different inefficient processes. Here is how low-code can help software developers:
Shorter development lifecycle: Low-code platforms come with pre-defined tools, reusable components, and templates that help to make application development faster. You can also do testing and integration more effectively with low-code.
Single code for all devices: Low-code applications translate to using standard technologies like HTML, CSS, and C#. The developers need not worry about the end-user platforms like web, mobile, and desktop. They only have to focus on building a single code that will work across devices and platforms.
What is the downside of low code solutions?
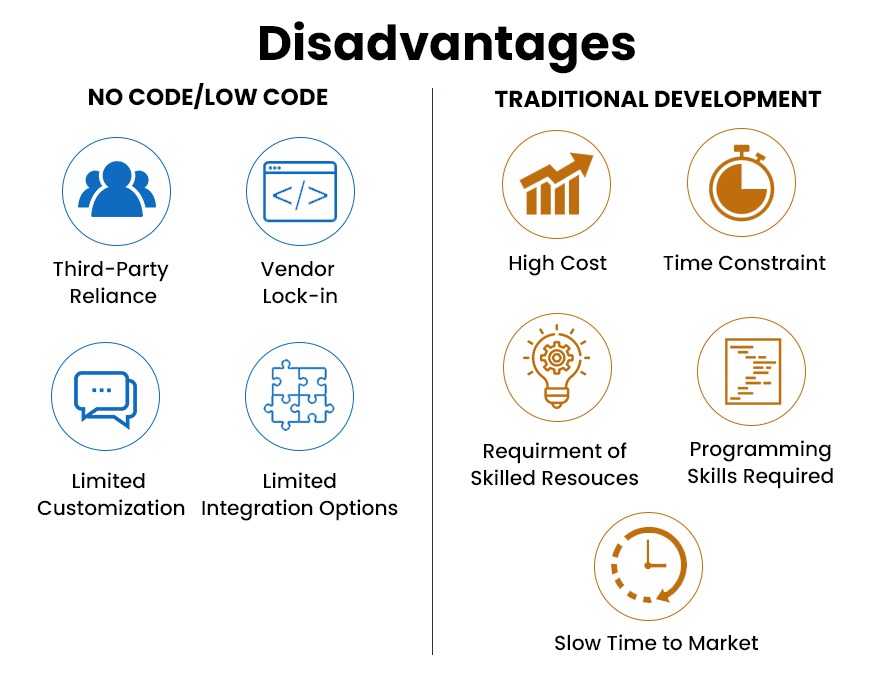
Since low-code platforms are provided by vendors, the big fear is vendor-lockin. However, this varies from vendor to vendor. Many vendors provide clean, standardized code that can work anywhere and so applications can work outside the vendor platform as well. However, some vendors don’t allow you to make changes to your applications once you stop using their tool. It is important to be clear on vendor terms before signing up.
Not all applications can be developed in low-code and knowing the difference is important. A business may not get the exact functionality they need with low-code, even though low-code platforms provide some level of customization. With custom software development, businesses can build any feature they need, the only limitation being time and cost. Custom software can be built with full flexibility, choosing the right technology stack, tools, and APIs. Custom software might be safer from hackers as cyber criminals might not be familiar with a customized application.
The technology trends indicate that hybrid systems will be the future i.e. low code solutions amalgamated with custom features. Talk to our experts on developing hybrid solutions that are form-fitted for your business requirements.




