
For healthcare providers, Health Level-7 (HL-7) integration is an important prerequisite in any healthcare software or process. HL7 is an international standard framework that helps healthcare providers share and receive patient information. There are three main components of a successful HL7 data transfer:
-
- 1. Transmitting data from one application or provider to another
-
- 2. Receiving and interpreting the data
- 3. The mode of transferring data.
While on the surface the process looks simple enough, HL7 integration could actually throw up a number of challenges. Some of the most common problems that could arise out of incorrect implementation are the need for double entry of data, data duplication and incorrect patient records being shared and stored. How do healthcare providers avoid these issues when setting up an HL7 integration with new software applications? Here are some of the most common HL7 integration challenges you should know about and how you can avoid them.
1. HL-7 integration can be a complex and time-consuming process
HL-7 integration is hardly an overnight process. Pre-existing software is typically enmeshed in a number of applications. Health Level 7 integration can, therefore, interfere with the normal functioning of other integrated software. This is why centers should have a dedicated project team to oversee the successful completion of HL7 integration. The team should work with in-house or external HL7 integration specialists like iTech, to trace every application and HL-7 interface engine connected with the software to ensure that there are no unforeseen disruptions.
Interoperability is critical when it comes to HL7 integration, so the project team needs to ensure that every endpoint for the new software or application should be compatible with existing applications and interfaces. In some cases, new endpoints might need to be created or existing ones modified. In case external vendors manage certain HL7 interface engines, they will need to be notified so they can modify their endpoints too.
Healthcare centers should be prepared well in advance for the long implementation and integration phase. As resources will most likely have to be diverted for the implementation, non-critical projects might have to be put on hold for some time.
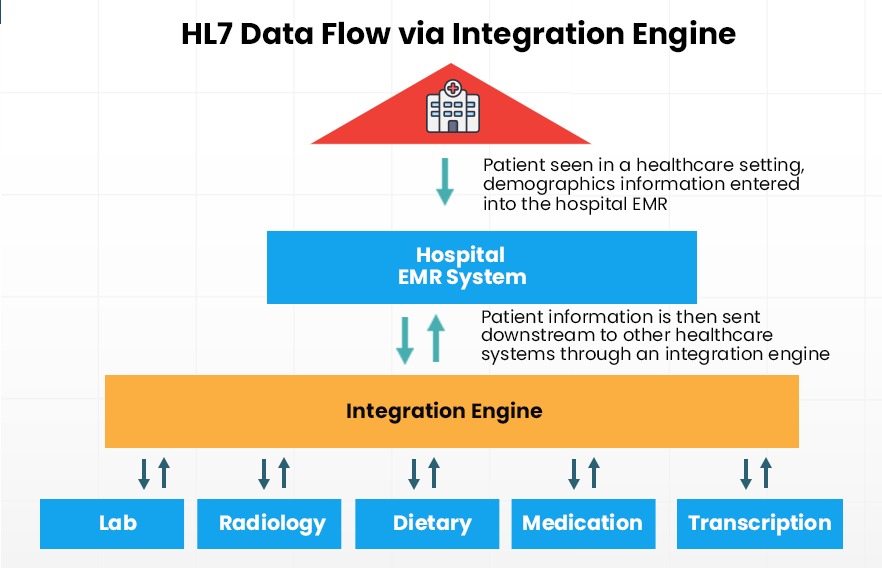
2. Inconsistent data semantics can cause ambiguity
Different applications could have their own understanding of what abbreviated health messaging means. A patient record can have a number of abbreviations and if all healthcare staff aren’t clear about their meaning, this could lead to misinterpretations and serious consequences.
A commonly cited example of ambiguous health messaging is the use of the abbreviation NA. In a patient record, NA could mean anything from Not Applicable to No Allergies. Clearly, both can vastly alter a patient’s treatment decisions.
Similarly, many healthcare clinics use a numeric key for a patient’s history. The number 2, for example, can indicate that a patient has a history of excess alcohol consumption. If these semantic frameworks aren’t carried over during the integration, there can be huge implications for patient care. Incorrect semantics in health messaging will also essentially render data records useless, which means staff will have to identify errors and re-enter values all over again. This will seriously impact staff productivity and efficiency in delivering patient care.
To avoid these pitfalls, it’s important that every HL7 interface engine not only transmits data but also understands what they actually mean. Data shared during integration should fit into a standard semantics framework. As healthcare becomes increasingly personalized with numerous touchpoints, accurate semantics records in HL7 will become even more critical.
3. Legacy data can be lost or corrupted during transfer
In any integration or migration project, there’s always a risk of data loss. In HL7 integrations, however, the potential data loss is especially critical because patient records are invaluable and contain sensitive information. To avoid the loss of EHRs, some clinics might have multiple EHR applications, but this isn’t an efficient solution. Staff will have to enter patient information into multiple systems, which is an inefficient use of time. Other clinics might maintain paper-based records, which isn’t a sustainable option either. Paper-based records are difficult to store and can be easily misplaced or damaged.
The fastest way to migrate to a new platform while maintaining integrity of patient information records is to conduct the migration in stages. First, only critical information such as past diagnoses, medication history and allergy information should be transferred. Then, less critical data such as old scans and lab reports should be moved. Migrating data in stages helps identify any issues in the transfer quickly and rectify them before the next batch of data is migrated. For instance, Images very often aren’t supported in certain software applications and if this isn’t identified quickly, the whole process will have to be restarted.
Health Level 7 integration is essential to encourage higher adoption of software applications. Even if the new application has several advanced features, healthcare staff will simply not use it if it means having to re-enter patient data. In recent times, particularly, healthcare workers are under immense strain and so applications need to facilitate and not hinder higher productivity.
While the above challenges are some of the most common ones that you should know of, there are smaller issues that can crop up during implementation. A dedicated project team with proven projects along with a proactive mindset can help you overcome these challenges and set up a successful integration. Through seamless HL7 integration, healthcare providers can ensure that their applications are easily accessible, have updated patient records, and do not require duplication of efforts.
Need an expert in HL7 integration?
Contact our team of experts today to see how we can help keep your systems running to provide a strong support to your services.





