
If you are looking for a cost-effective quick fix then custom software will not meet these objectives. Custom business tools by the very definition are built to solve unique challenges that your business faces and will need a greater investment to build.
In the case of SaaS software, while there are many advantages, the cons are that either you try to fit your business requirements to the features the ready-made solution provides or try to add customization to it. However, a SaaS product is not meant for extensive customization and can take time. New technology upgrades might see your solution fail. It can end up being very expensive in the long run and the cost efficiency benefit will soon be non-existent
Off-the-shelf. SaaS or packaged software is built for the mass market while custom software is built for the unique needs of a company.
When is Custom Internal Tool more suitable?
While there is no doubt that off-the-shelf software is good based on your requirements, there are certain situations where you might opt for custom software.
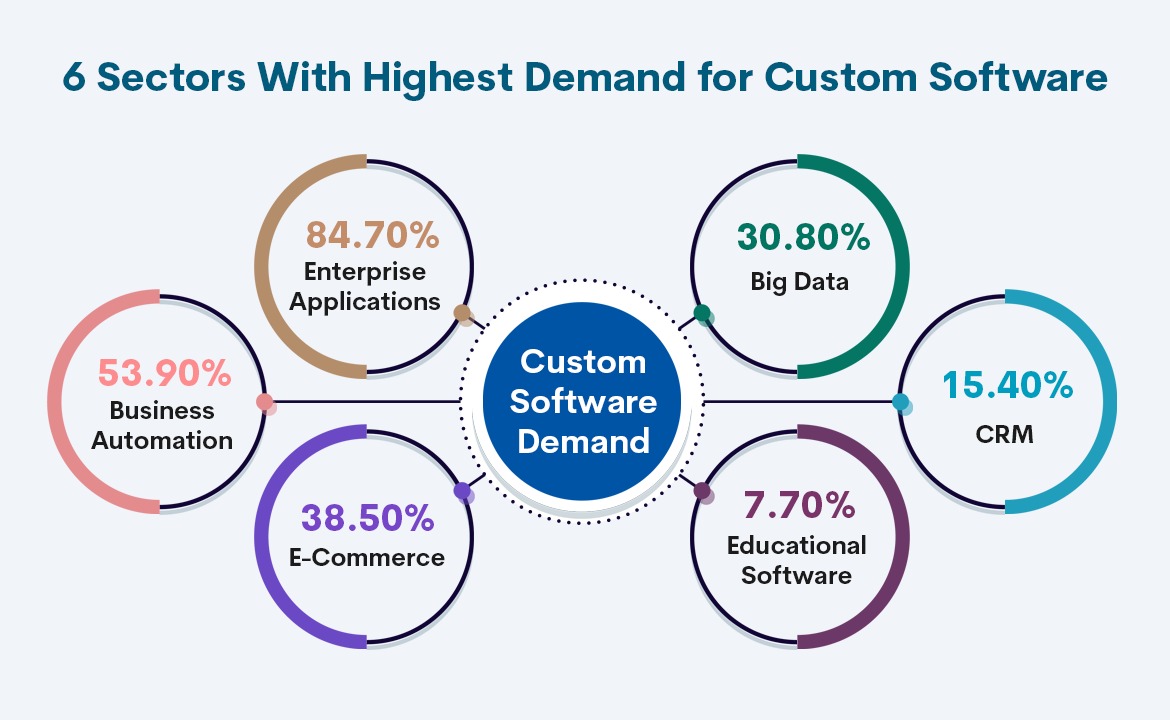
Here’s a comparison of what SaaS tools can provide versus how custom software can go beyond, specifically for these 7 industry use cases.
1.Human Resources Management
SaaS Tool: A SaaS HR management tool can offer standard features like employee data management, time-off tracking, and basic reporting.
Custom Software: Custom software can provide additional functionality, such as integration with payroll systems, advanced performance evaluation modules, customized workflows for talent acquisition, and specific compliance requirements for industries with unique HR regulations.
2.Sales and CRM
SaaS Tool: A SaaS CRM tool offers basic contact management, sales pipeline tracking, and standard reporting capabilities.
Custom Software: When an organization decides to build software it is because the custom software can provide industry-specific CRM modules, customized sales processes, advanced analytics, integration with external systems (e.g., ERP), and personalized dashboards tailored to the specific sales needs of the organization.
3.Financial Management
SaaS Tool: A SaaS financial management tool can provide standard accounting functionalities, such as general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, and basic financial reporting.
Custom Software: Financial management capabilities can be extended by incorporating industry-specific financial modules (e.g., fund accounting for non-profits), complex budgeting and forecasting tools, integration with third-party systems (e.g., banking APIs), and customized financial analysis and performance tracking.
4.Legal Services
SaaS Tool: Legal practice management software can offer basic features such as case management, document storage, and time tracking.
Custom Software: Custom build software can provide additional functionality like automated document generation, integrated legal research tools, customized workflows for different practice areas, and compliance tracking specific to legal regulations. Read iTech’s case study for the very first AI-powered software for immigration attorneys in the US.
5.Real Estate
SaaS Tool: Real estate management software can provide basic features like property listings, tenant management, and rent collection.
Custom Software: Custom applications can go beyond by incorporating functionalities such as automated lease agreement generation, integration with property listing websites, advanced analytics for property performance evaluation, and customized reporting for property owners and investors.
6.Hospitality
SaaS Tool: Hotel management software can offer standard features for reservations, guest check-in/check-out, and basic reporting.
Custom Software: Custom applications can provide tailored solutions with additional capabilities like integration with key card systems and POS systems, personalized guest preferences and loyalty program management, dynamic pricing algorithms, and customized reporting for revenue management.
7.Insurance
SaaS Tool: Insurance agency management software can provide basic features like client policy tracking, commission management, and basic reporting.
Custom Software: Many insurtech vendors are building software to extend functionalities by incorporating features like automated underwriting and claims processing, integration with insurance rating systems, advanced analytics for risk assessment, and customized reporting for compliance and regulatory requirements.
Also Read: SaaS vs Custom Based Solutions – The Pros and Cons
As you can see custom build software allows for the development of specialized solutions that align with industry-specific needs, regulatory compliance, and unique workflows. By going beyond the capabilities of standard SaaS tools, custom applications can enhance efficiency, provide a competitive edge, and cater to the specific demands of the respective industries.
When building your internal business tool – a few pointers
You have a problem that no existing software can fully resolve, you need to build a solution that many users will utilize – that is the classic triumvirate for a custom software solution. It holds true whether your organization has its own extensive IT team or like most businesses, you choose an external software development company.
You have a problem that no existing software can fully resolve, you need to build a solution that many users will utilize – that is the classic triumvirate for a custom software solution.
- Clearly define the problem or challenge that the tool aims to solve. Understand the specific needs and pain points of your business or team that the tool should address and focus development efforts on a solution that directly addresses those needs.
- What specific outcomes or improvements are you looking to achieve? Define measurable goals that will allow you to evaluate the success of the tool once it’s implemented.
- Engage key stakeholders throughout the development process. Collaborate with the end users, managers, and other relevant individuals who will be using or benefiting from the tool.
- Decide who knows the problem best to collaborate with the team that is building the solution.
- Design the tool with a focus on simplicity, intuitiveness, and efficiency. The tool should be easy to learn and use, reducing the learning curve for new users.
- Consider the scalability and flexibility of the tool. As your business grows and evolves, the tool should be able to accommodate changing needs and increasing demands. Build a modular and extensible architecture that allows for easy updates, integrations with other systems, and future enhancements.
- Depending on the nature of the data being handled by the tool, ensure appropriate security protocols are in place to protect sensitive information. Implement user authentication, data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of the tool and its data.
- Consider organizing training sessions or workshops to familiarize users with its features and capabilities. Ongoing support and assistance should also be available to address any user questions or concerns.
- Allocate resources for regular maintenance and updates of the tool.
Internal tools are a powerful way to increase efficiency and boost productivity for your organization. Talk to our senior management about a custom software development project you want to build. Here are some of our case studies to showcase the unique software solutions we have developed.






