
The healthcare industry is a prime target for cybercriminals due to the high value of patient data. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, with hackers employing sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities. This translates into a multi-pronged strategy by healthcare organizations in protecting patient data, adapting to new threats, and implementing advanced cybersecurity measures to counteract emerging risks. HIPAA protected healthcare regulations make the measures detailed here mandatory for healthcare organizations in America.
Cybersecurity in healthcare is critical due to the following reasons
Preventing Healthcare Data Breaches – Data breaches in the healthcare sector can have severe consequences. Cybercriminals target healthcare organizations to steal patient data, which can be exploited for financial gain, fraud, or identity theft. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, healthcare organizations can make it tougher for data breaches and protect patients from potential harm. These policies should align with industry standards and regulations.
The healthcare sector is a prime target for cybercriminals. A Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report found that 30% of all data breaches analyzed were in the healthcare industry.
Protecting Patient Privacy – Healthcare organizations collect, store, and transmit vast amounts of sensitive patient information, including personal, medical, and financial data. Maintaining the privacy and confidentiality of this data is crucial for patient trust and compliance with privacy regulations such as HIPAA. Cybersecurity measures help prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft, ensuring patient privacy is safeguarded.
Safeguarding Patient Safety – Cybersecurity incidents in healthcare can disrupt critical systems and services, potentially impacting patient safety. For example, if hackers gain unauthorized access to medical devices or systems controlling patient care, they may manipulate or disable them, endangering patient well-being. Ensuring the security and integrity of healthcare systems is essential for maintaining patient safety and preventing adverse outcomes.
Cybersecurity incidents can have a direct impact on patient safety. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) reported cases where cyber incidents, such as ransomware attacks, led to the disruption of critical services and patient care.
Preserving Healthcare Operations – Healthcare organizations rely heavily on information systems and technology to deliver quality care. A cyberattack or security incident can disrupt operations, leading to downtime, loss of patient records, and compromised access to critical healthcare services. Cybersecurity measures help minimize these risks, ensuring continuity of care and preserving the efficiency of healthcare operations.
Complying with Regulatory Requirements – The healthcare sector is subject to various privacy and security regulations, including HIPAA in the United States. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in legal and financial penalties. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential for meeting regulatory requirements and demonstrating a commitment to protecting patient data.
Combating the Evolving Threat Landscape – The healthcare industry is a prime target for cybercriminals due to the high value of patient data. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, with hackers employing sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities. Healthcare organizations need to stay vigilant, adapt to new threats, and implement advanced cybersecurity measures to counteract emerging risks.
Maintaining Trust and Reputation – A data breach or cybersecurity incident can significantly damage the reputation of healthcare organizations. Patients trust healthcare providers with their sensitive information and expect it to be kept secure. By prioritizing cybersecurity, healthcare organizations can demonstrate their commitment to patient data privacy and maintain the trust and confidence of their patients.
Also Read: How AI is assisting EHR Data organization in Medical Practices
Measures to Deter Healthcare Data Breaches and Prevent Threats in EHR
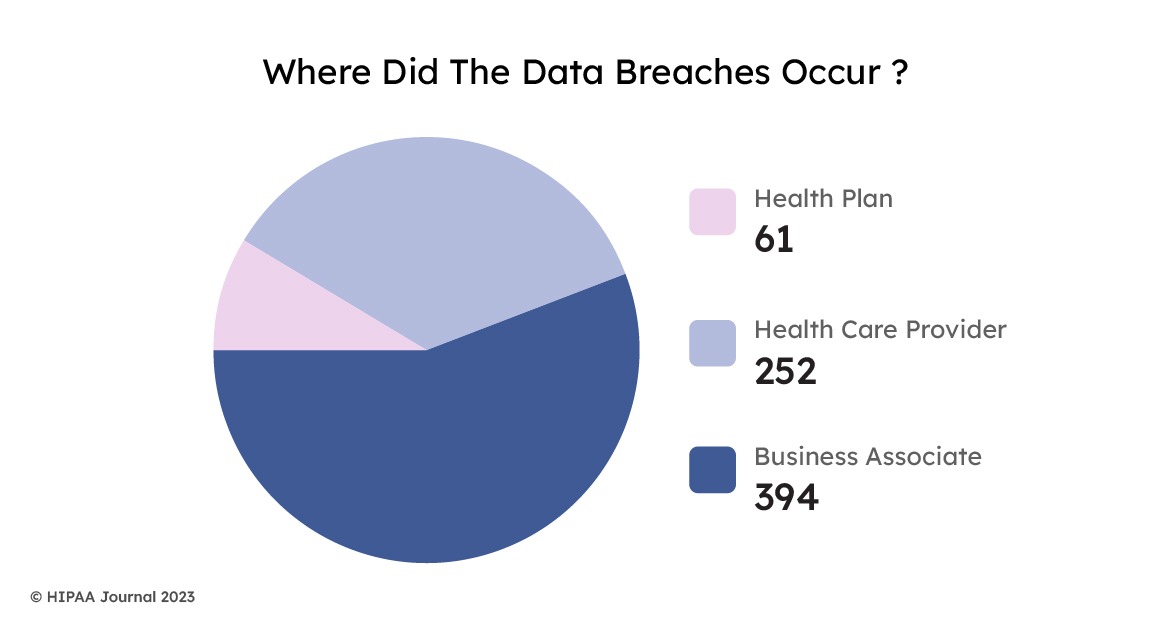
EHRs play a critical role in modern healthcare, as they digitize and centralize patient health information. However, the downside of connected systems is that hackers can worm their way in. Electronic Health Records EHR security concerns must be addressed through specific cybersecurity measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient data.
Also Read : 5 Healthcare Cybersecurity Strategies to Prevent Cyberattacks
Here are 11 Key Considerations for EHR Cybersecurity Best Practices
1. Risk Assessments of Healthcare Workflows: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats to patient data. This involves assessing the security controls, systems, and processes in place to identify areas of weakness and prioritize security improvements. This includes both internal (e.g., employee errors) and external (e.g., hacking) threats. Ensure that the risk assessment process aligns with relevant regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), which mandates risk assessments for protected health information.
2. Access Controls for EHR Security Concerns: Implement strong access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access patient records. This includes unique user IDs, strong passwords, and multi-factor authentication. Role-based access control should be employed to restrict access to specific information based on job responsibilities.
3. Data Encryption in EHR: Encrypting patient data both in transit and at rest is mandatory. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals, it remains unreadable and unusable. Data encryption in EHR solutions should be used for data transmission between systems, as well as for data stored on servers, databases, and mobile devices.
Also Read: Superpower your EHR- Challenges and Opportunities for AI Integration in EHR Systems
4. Regular Patching and Updates: Keep EHR systems and software up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Regularly patching vulnerabilities is crucial to prevent exploits and protect against known threats. Ensure that you associate with a technical partner or EHR vendor that has this as part of your agreement.
5. Network Security: Implement robust network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and intrusion prevention systems. These tools help monitor and control network traffic, detect suspicious activities, and prevent unauthorized access to EHR systems. The infographic below indicates that most data breaches occur through the network severs with EHR breaches coming third.
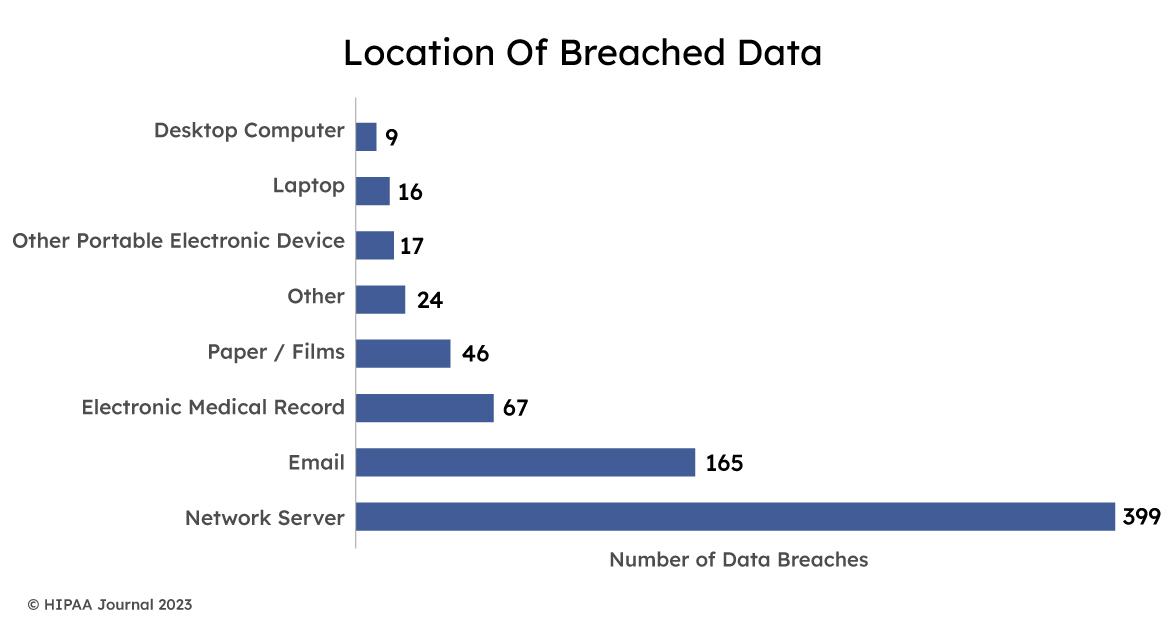
6. Employee Education and Training: Provide comprehensive cybersecurity training to all staff members who handle EHRs. Weak human practices are one of the biggest EHR security concerns. Employees should be educated about best practices for password management, phishing prevention, and the importance of data privacy. Regular training sessions and awareness campaigns can help mitigate human errors and prevent data breaches.
7. Incident Response and Data Backups: Nothing is failsafe so develop a robust incident response plan to address cybersecurity incidents promptly and effectively. Regularly backup EHR data to ensure data availability in the event of a security breach or system failure. Test data restoration procedures to ensure backups are valid and accessible when needed.
8. Vendor Management: If you use third-party vendors for EHR services, conduct due diligence to ensure they have robust cybersecurity measures in place. Assess their security protocols, data protection practices, and compliance with privacy regulations to minimize risks associated with outsourcing EHR services. Talk to iTech about our RehabONE EHR platform and our robust HIPAA compliant cybersecurity that adheres to healthcare best practices.
9.Compliance with Privacy Regulations: Stay informed and compliant with relevant privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Understand the requirements and ensure your EHR systems and practices align with these regulations.
10. Security Audits and Assessments: Regularly conduct security audits and assessments of your EHR systems to identify vulnerabilities and gaps in your cybersecurity defenses. It does not matter how large or small your practice is, patient data privacy is critical. These audits can help you proactively address potential threats and enhance the overall security posture of your organization. It doesnt
11. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Intelligence: Implement continuous monitoring systems to detect and respond to potential threats in real time. Stay updated with the latest cybersecurity threats and trends in the healthcare industry through threat intelligence sources. This information can help you proactively address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
By implementing these measures, healthcare organizations can enhance the security of their EHR systems, protect patient data, and mitigate the risks associated with cyber threats. It is important to adopt a holistic approach to cybersecurity, involving technology, policies, procedures, and employee awareness to create a robust and secure environment for patient information. Talk to our iTech healthcare experts if you have concerns about your existing EHR systems.





