
Manual prior authorizations cost providers $10.26 per transaction compared with $3.64 per electronic translation – 2020 CAQH Index Report
Why automating the pre-authorization process is not straightforward
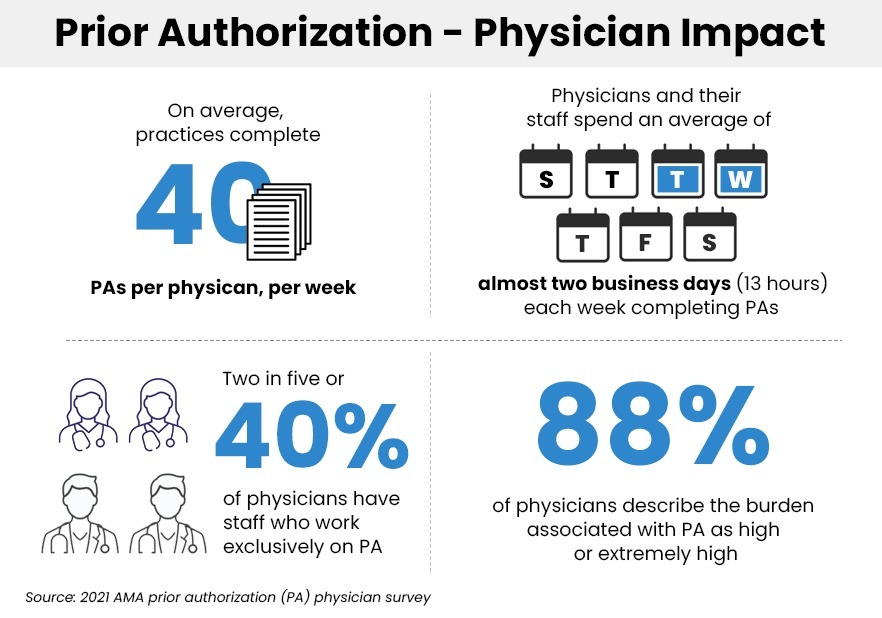
There are a number of reasons that make the process so complicated:
- There are a lot of steps involved in insurance verification and upping the antenna for possible error and potential delays
- The payer (insurance carriers) and the providers (healthcare) do not have a standardized workflow.
- Payer rules are constantly changing and it is hard to monitor them and make revisions.
- It is further complicated by thousands of payers and health plans. Payers can keep adding to their health plans
- Shortage of skilled staff means that experienced hands might not be available
Many technology providers claim they have an automated solution that reduces the complexity involved in pre-authorization but many automate a few steps in the process. iTech India is a technology provider that has implemented automated solutions with their data services benefits verification team. This is a team that works on pre-authorization and benefits verification for Healthcare clients in the U.S. Having a custom software company as part of the group means that the parent company develops the software systems for the Data Services team. The proof of the pudding is after all in the eating and with healthcare clients that have been with us for over 13 years, it speaks for a proven pre-authorization automation solution that delivers results.
4 Benefits of Automating Prior Authorization Process in Healthcare
Here are 4 specific benefits that automation brings to the benefits verification process:
1. Automatically update rules and requirements
In the manual process, payers’ websites would have to be continuously checked for changes in forms and rules. This method is time-consuming and highly prone to error. The benefit of automating this process is that the software will continuously scan the rules of tens of thousands of health plans. When it notices any change by comparison to previous rules then an alert is created and the necessary information to comply with the new rules is gathered from the patient’s medical records within the EHR.
2. Reduces denials and write-offs and improves revenue
If the prior authorization process includes automated tools then it would capture the specific requirements of the payer and will enter it electronically into the provider’s medical billing software system. It ensures compliance with service level agreements and this helps reduce the risk of denials and reduces the loss of revenue through write-offs. Breakdowns in the prior authorization process can cause up to 30% of preventable write-offs.
3. Automation can track every authorization from end-to-end
Many benefit verification systems may use RPA (robotic process automation) to check status changes. While it can power repetitive work, it has a limitation. RPA bots are rule-based and follow a specific set of laid-out steps. In case, an EHR user interface changes or if an insurance website gets updated then the bot needs to be updated as well since it is programmed to look at a specific place on a screen for information. This means that RPA tools need high maintenance. AI-powered automation, on the other hand, is judgment-based. For instance, it can make status checks on insurance portals and update you when an authorization is made.
4. Improves patient experience
The healthcare revenue cycle has a direct bearing on patient satisfaction. Even if they are getting the best medical advice, a negative experience with the medical billing department can cause unnecessary frustration. Patients expect their benefits to be checked accurately and not to be hit by any unexpected costs. What automation does is ensure faster and more accurate authorization and get patients the medical assistance they need.
Contact us for a demo on exactly how outsourcing to the iTech India benefits verification team can streamline and automate your prior authorization process.









