
In 2020 and 2021 many businesses were forced to quickly shift to remote work and later hybrid working conditions. What this meant was a quick transition from the fairly secure office environment to personal laptops and mobile devices for work processes. This opened up many companies to cyber attacks. This is supported by information from SpyCloud for the year 2021 – The company recaptured more than 1.7B credentials (compared to 1.46B in 2020) and 13.7B pieces of PII (personally identified information) from the cybercriminal underworld.
So what do you know about the modern cybersecurity trends for mobile applications? If it is a grey area for you, this article will help with some useful mobile app security tips to keep abreast of the ever-evolving murky work of cybercriminals.
Cybersecurity trends in 2024 and beyond
In 2021, the Amazon Ring app accidentally revealed the location of the people using the app to monitor their property through security cameras, Ring video doorbells, alarm systems, and smart lights. While the loophole was fixed quickly, there was still a space when hackers could access the wi-fi credentials of the app members and compromise their other devices. When such big tech companies can develop apps with security flaws that make it even more vital for security to be built in from the initial stages of app development. Here are the cybersecurity trends predictions for 2024 and beyond.
1. Careless use of third-party app software: Open source libraries and APIs, also called public APIs, are application programming interfaces that are freely shared on the internet allowing anyone to access them and use them in their own websites and mobile applications. While these public APIs do wonders for reducing development time and adding new functionality, there might be security risks from components that have some code vulnerabilities. Some examples of public APIs are social media bots, weather apps, Google Maps, etc. Careless use of open source tools and third-party apps can open mobile apps to possible criminal activity.
2. DevOps and Cloud Systems: The Cloud offers tons of storage and the environment needed for process automation. DevOps and the Cloud are becoming intertwined tools that more and more businesses are utilizing. DevOps is an amalgamation of business philosophy, practices, and tools that increase the organization’s capability to deliver applications at a very high velocity. However, the downside is that they can put businesses at risk of third-party vulnerable code. And with cyber hacks going after vulnerabilities this is a risk that needs to be addressed.
3. Code injection attacks: Hackers will inject malicious lines of codes through login forms to access business data. In a code injection attack, an attacker will supply untrusted input into a program, changing the way the program executes. It can then execute operating system commands with the privileges of the user who runs the web application. One of the common mobile application development issues is the failure to limit the characters that can be entered into the input field allowing codes to be injected.
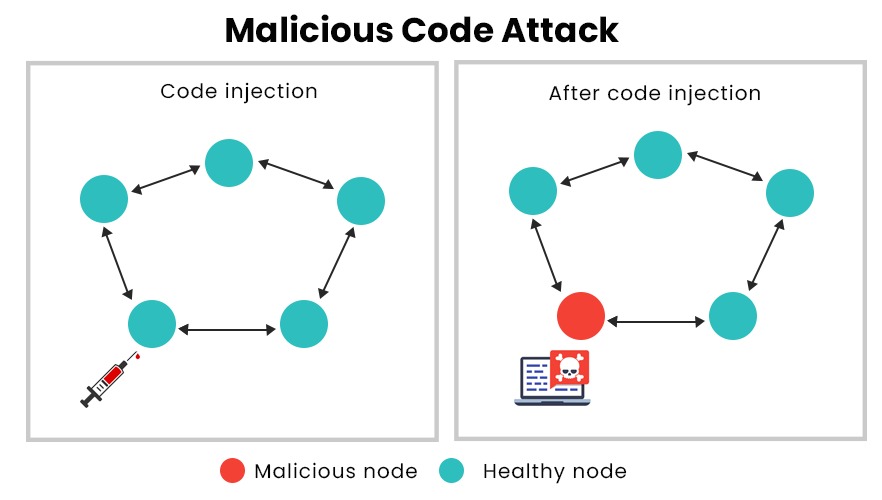
App security best practices that must be followed
Data theft is a cash cow for cybercriminals and they keep finding new ways to do this.Mobile application development must make it as difficult as possible to do this.
-
- Write secure code: This starts with architecting and designing for security policies. Also, always validate input from an untrusted source. Keep design simple since a complex design can increase the chances of error in its configuration, implementation and use. This means that as code gets added on, more time should be spent cleaning it up. Adhere to the principle of least privilege for a limited time. This prevents hackers from elevated privilege access and time to inject spurious code.
The principle of least privilege is that an object must be given only that privilege needed to complete a task.
-
- Encrypt data: Encryption will scramble text and this will prevent unauthorized access except by users who have the key. Encryption transforms data from human-readable plain text into non-human readable cipher text. The main goal of data encryption is to prevent unauthorized parties from gaining access to sensitive information.
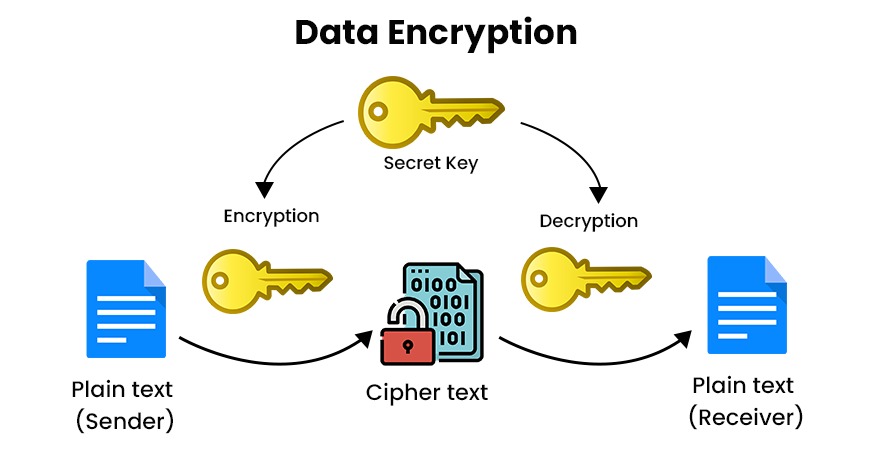
-
- Test code of third-party libraries: Third-party applications provide users with pre-tested reusable code. However, criminals can identify common vulnerabilities in open-source libraries. Developers should reduce risk during mobile application development by isolating code from third-party tools as much as possible.
- Only use authorized APIs: Since APIs are the communication protocol between 2 different systems and pass sensitive data, it makes it important to have barriers up. Be careful to stay away from unauthorized APIs as they might not have sufficient security in place. Whatever the third-party tools, always have in place ways to limit the attack. For instance, limit response data to prevent code injection. Another example to ensure application security is to prevent a DDoS attack (distributed denial of service that plays havoc with normal traffic). The app should limit payload size and also ensure rate limiting for APIs. Rate limiting puts a cap on how many times someone can repeat an action within a certain timeframe.
Rate limiting puts a cap on how many times someone can repeat an action within a certain timeframe.
- Use tamper-detection technology: This application security technology will detect when your app is compromised. When this happens, an alert is immediately sent out to app monitors. Also because tamper-detection technology works in the app environment when it detects something unusual it will immediately launch defensive actions. One of these is to immediately terminate a session that shows suspicious activity,
Use tokens to identify sessions: A session is defined as the time the user spends on your app in one visit. Normally, sessions are long on mobile devices, making them vulnerable. It is important to identify each session with a token so that your company can revoke a token anytime suspicious behavior is identified or can force a log-off in case a device is stolen or lost. - Utilize updated cryptography tools: It is also important in application security to use the latest cryptography tools because older ones might not have modern technology. For example, Security Tokens/Authentication Tokens are a cryptography tool to authenticate users. Docker is another cryptography tool that creates a container in which an application can be developed. Not only the data but also the files are kept in an encrypted form.To get started on building your app idea or updating your existing app,talk to our app specialists to get a head start on building security into your mobile application development. iTech is a HIPAA-compliant and GDPR-compliant company and is also AICPA SOC certified.






